Around the globe, nations are grappling with water scarcity driven by climate change, urbanization, and resource exploitation. To combat this, large-scale groundwater restoration projects are underway, replenishing depleted aquifers and securing water for millions. However, emerging evidence reveals an urgent and global challenge: the unintended seismic risks posed by rising sea level rise, groundwater tables, and specifically the amplification of earthquake-induced soil liquefaction.
Liquefaction transforms stable soil into a fluid-like state under seismic stress, and rising groundwater levels significantly increase this risk. Data from seismic zones worldwide—from New Zealand and the United States to Japan and beyond—show a direct correlation between shallow water tables and liquefaction damage, including foundation collapses and infrastructure failures. With many restoration projects targeting regions prone to earthquakes and urban development, this risk is fast becoming a global concern.
Seismic vulnerability mapping must be integrated into groundwater management plans to prevent amplified risks in urban environments. International collaboration must prioritize research to forecast and mitigate liquefaction hazards as groundwater projects expand and disaster risk reduction frameworks—such as the Sendai Framework—must evolve to encompass the complex interaction between groundwater changes and seismic impact.
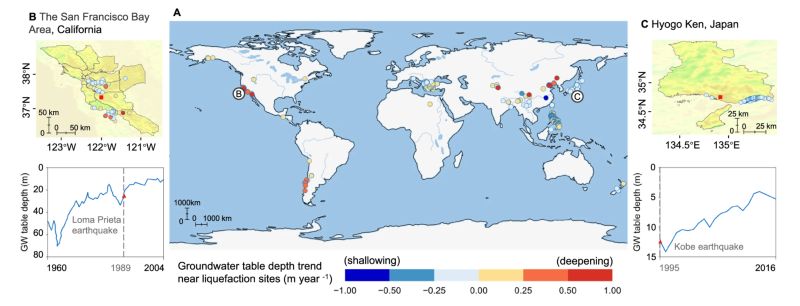
Fig: A Reported liquefaction sites17,25 and corresponding Groundwater (GW) table depth trend in the twenty-first century21,26,58. The scattered circle point represents the location of the liquefaction site and the color shows the trend of GW table depth. B Liquefaction sites in the San Francisco Bay area, USA, and GW table depth change (at the red square location in the map). C Liquefaction sites in Hyogo Ken, Japan17,25, and GW table depth change (at the red square location in the map).
#GroundwaterManagement #SeismicRisk #SoilLiquefaction #UrbanResilience #ClimateAdaptation #DisasterRiskReduction #SendaiFramework #EarthquakePreparedness #SustainableWater #InfrastructureSafety